Arbitrum is one of the prominent EVM-based Layer-2 blockchains with a high network capacity and low costs. The ARB token is used to participate in Arbitrum’s governance and has a central role in its blockchain.
We estimate ARB to be a sustainable investment in the long term but its value may not gain much due to the huge number of unlocked and uncirculated tokens that will enter circulation in the future.
Purpose and Use Cases
Arbitrum’s main purpose is to provide an alternate way to transfer ETH and Ethereum-based assets like cryptocurrencies (ERC-20) and NFTs (ERC 721 and 1155).
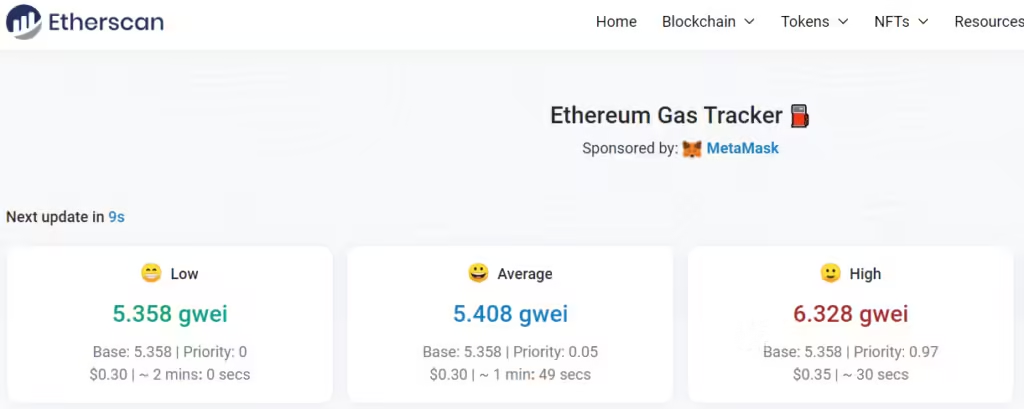
The reason why Ethereum users need Layer-2 scaling solutions like Arbitrum is because of relatively higher fees in Ethereum. Even at its lowest, a transaction in ETH costs around 30 cents. Though it seems less, it’s still too expensive for daily usage. For example, if I buy a $1 candy or a $2 newspaper, the transaction cost would alone cost 30% and 15% of the transaction value respectively.
On the other hand, a token transfer on the Arbitrum blockchain costs less than 1 cent.
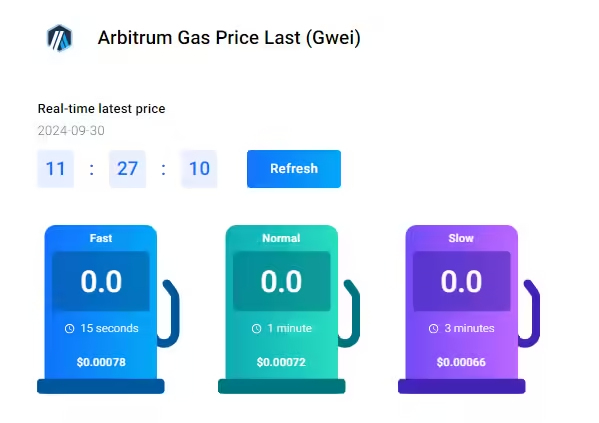
This makes Arbitrum a low-cost solution for Ethereum-based tokens, NFTs, and other assets.
Now, if you feel concerned about security, the Arbitrum blockchain sends a summary of these transactions to Ethereum from time to time so that ETH can verify the validity of all transactions through a method known as the Merkle Tree.
How Does Arbitrum Work?
Arbitrum uses a zero-knowledge-based solution called Optimistic Rollup to summarize its transactions and sends this summary to Ethereum. Once Ethereum sees this summary, it checks its validity through the Merkle Tree. Even if one transaction is invalid, the Merkle Root of the summary of transactions will differ from the calculated Merkle Root by Ethereum validators.
Here is a stepwise demonstration of how things work on Arbitrum.
- 1. Firstly, a user generates a transaction.
- 2. The Arbitrum blockchain then collects these individual transactions from multiple users and puts them inside a block.
- 3. The summary of this block is then generated and submitted to Ethereum.
- 4. Once Ethereum validates this summary, all the transactions in the block are validated and finalized.
Before the Dencun Upgrade, these summaries were processed as individual transactions on the Ethereum blockchain. However, after the upgrade, there is one more step added to the above steps to make transactions faster and even cheaper.
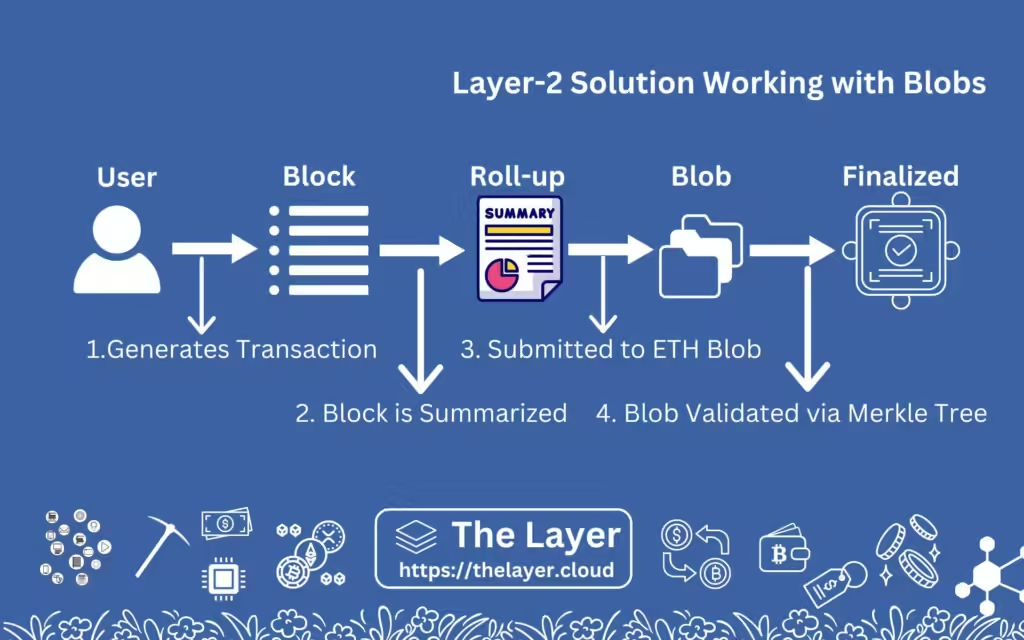
This new feature in Ethereum is called “Blobs”, which are temporary space built on Etheruem blocks that stores the summary of Arbitrum (and other L2) blocks. Summary data is now sent to these blobs, verified only via a Merkle Tree method, and if found valid, are finalized.
Technology and Infrastructure
Arbitrum One is a layer2 Ethereum scaling solution. It processes transactions using optimistic rollups and uses Ethereum as the final execution layer to reduce costs.
- The blockchain has a theoretical TPS of 40,000 transactions per second.
- Realistically, the used TPS is around 20 to 25 TPS.
- Maximum Recorded TPS on the Arbitrum One chain was at 896 TPS.
Tokenomics
Arbitrum has a current circulating supply of 3.6 billion ARB and a maximum supply of 10 billion ARB. With less than half of the tokens in circulation to date, investing in ARB does come with shocks.
Further, ARB has a very frequent unlock schedule. Each month the token unlocks 92.65 million ARB on the 16th of the month, representing 2.5% of the current circulating supply.
The Token Distribution is as follows:
- Arbitrum DAO – 42.7%
- Team (Present and Future) – 26.9%
- Investors – 17.5%
- Retail Wallets – 11.6%
- Arbitrum-based DAOs – 1.1%
We can infer from the above token distribution that most of the tokens, around 87.1% are in the hands of a few people, making it extremely vulnerable to price manipulation.
Such price manipulations are usually seen during bad markets when the fate of most cryptocurrencies keeps hanging by a thin thread. During those times, token manipulation could possibly dilute or even erase the little value you have in your hands.
Revenue and Economic Sustainability
Arbitrum uses optimistic rollups to summarize its block data. This summarized data is then put into Ethereum blobs (earlier fed into call data) which are then validated. This submission is necessary to validate roll-up transactions and requires it to spend money on L1 Fees (Blobscriptions).
Arbitrum One processes around
SWOT Analysis
Strengths
Arbitrum is a leader among L2s and has a decent market share of 37.6%. It is larger than all other layer-2 blockchains.
Abitrum One has the highest TVL among Layer-2s at $13.67 billion.
Weaknesses
The high volume of uncirculated tokens (64%) that could enter circulation in the future poses a serious threat to retail investments and with each unlock this invested value shrinks.
The second weakness comes from the high number of tokens (87.1%) in the hands of the internal team and investors makes the token susceptible to manipulation. On a secondary level, it also erodes investor confidence.
Opportunities
As VanEck predicts a $1 trillion Layer-2 market, the 103% growth rate seems pretty attractive.
The growth of Ethereum-based transactions would lead to an increase in L2 demand over time.
Use cases like day-to-day crypto transactions would necessitate the use of a Layer-2 solution like Arbitrum to keep transaction costs low.
Threats
Too high external competition among layer-2 solutions poses a serious threat. With heavyweights like Coinbase (Base blockchain), MetaMask (Linea blockchain), and Shiba Inu (Shibarium blockchain) entering the markets, it would be impossible to compete with them and remain relevant.




